Introduction
Radio galaxies and radio quasars emit radio waves as synchrotron
radiation from relativistic electrons spiralling in a magnetic field.
At least in the radio lobes, where the source is optically thin at most
observing frequencies, the radio spectrum can often be described by a
power law over a reasonable range of frequencies, and it is often
assumed that both the original radio spectrum and the distribution of
electron energies was a power law. Energy losses, most pronounced at
high electron energies, cause the spectrum to deviate from its initial
shape, causing a steepening of the high-frequency spectrum (eg. Myers
& Spangler 1985; Tribble
1993, hereafter Paper I). The two standard models assume either
that electron pitch angles remain constant (the KP model - Kardashev
1962; Pacholczyk 1970), or that the pitch angles are rapidly
isotropized by scattering (the JP model - Jaffe & Perola 1973).
The difference in pitch angle behaviour between the simple KP and JP
models leads to substantial differences in the resulting synchrotron
spectra. In the JP model, each electron has sampled all possible pitch
angles  because its pitch
angle has been continually randomized by the scattering. The total
losses are then the instantaneous losses B^2sin^2
because its pitch
angle has been continually randomized by the scattering. The total
losses are then the instantaneous losses B^2sin^2 , averaged over all pitch angles
to give B^2<sin^2
, averaged over all pitch angles
to give B^2<sin^2 >, and are independent of an electron's
current pitch angle. There is a sharp cutoff in the energy spectrum at
a break energy
>, and are independent of an electron's
current pitch angle. There is a sharp cutoff in the energy spectrum at
a break energy 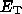 that is independent of
pitch angle or viewing orientation. The resulting spectrum is sharply
cut off at a frequency
that is independent of
pitch angle or viewing orientation. The resulting spectrum is sharply
cut off at a frequency 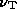 = c_1 B
= c_1 B
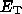 ^2 sin
^2 sin where B is the field strength and
c_1 is a constant (Pacholczyk 1970). There is little variation of the
spectrum with viewing angle so that averaging over different
orientations of the field gives a total spectrum that retains the sharp
cutoff.
where B is the field strength and
c_1 is a constant (Pacholczyk 1970). There is little variation of the
spectrum with viewing angle so that averaging over different
orientations of the field gives a total spectrum that retains the sharp
cutoff.
In the KP model there is still a sharp break in the energy spectrum at
a given pitch angle, but the break energy 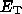 depends on the pitch angle
depends on the pitch angle  because the losses are strongly dependent on pitch angle - the
sin^2
because the losses are strongly dependent on pitch angle - the
sin^2 factor is not averaged
away. At a given field orientation, the spectrum is sharply cut off.
Integrating over all field orientations eliminates the sharp cutoff in
the spectrum because the total spectrum includes contributions from
electrons with all pitch angles, which have a wide range of break
frequencies. In particular, the electrons with very small pitch angles
have very low losses and a correspondingly high
factor is not averaged
away. At a given field orientation, the spectrum is sharply cut off.
Integrating over all field orientations eliminates the sharp cutoff in
the spectrum because the total spectrum includes contributions from
electrons with all pitch angles, which have a wide range of break
frequencies. In particular, the electrons with very small pitch angles
have very low losses and a correspondingly high 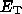 and
and 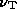 , so that while at
high frequencies the radiation from the electrons with large pitch
angles has faded, we still see the emission from the electrons
travelling at very small angles to the field.
, so that while at
high frequencies the radiation from the electrons with large pitch
angles has faded, we still see the emission from the electrons
travelling at very small angles to the field.
The JP model has a much more secure physical basis than the KP model.
The electron pitch angle distribution in the KP model is anisotropic -
such a pitch angle distribution is unstable as it excites Alfvén
waves which scatter the electrons back to an isotropic pitch angle
distribution (Wentzel 1969; Melrose 1980). Inverse Compton scattering,
variations in field strength and direction, and any waves generally
present in the relativistic radio plasma will also isotropize the
electron pitch angle distribution. Thus the JP model should give a much
better description of aged radio spectra than the KP model.
Unfortunately, detailed multifrequency observations of Cygnus A
(Carilli et al. 1991) supported the KP model, not finding the extremely
strong break in the spectrum predicted by the JP model.
Furthermore, Katz-Stone, Rudnick & Anderson (1993) analysed the
Cygnus A spectra and questioned the assumption that the spectral shape
was due to ageing of an underlying power law spectrum. They introduced
the concept of the radio colour-colour plot and proposed that it could
be a useful diagnostic tool for studying radio spectra. They showed
that the traditional radio spectral models (specifically the simple JP
and KP models) do not give a good description of the spectrum of
Cygnus A, and argued that the spectral shape was not solely due to
ageing effects. If this is true, it would require a radical revision of
the standard assumptions used in spectral ageing analyses.
However, realistic models of the ageing process give spectra with a
variety of shapes (see Paper
I). These models allow for the effects of a spatially varying
magnetic field, inverse Compton losses, and diffusion of electrons
between regions of different field strength. The general effect is to
smooth out the sharp spectral break of the JP model by superposing the
spectra from regions where the physical conditions cause the break
frequency to differ. The variation in break frequency is caused by
spatial variations in energy losses which set the energy 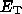 at which the energy spectrum breaks, and by variations
in magnetic field strength which convert the break energy
at which the energy spectrum breaks, and by variations
in magnetic field strength which convert the break energy 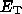 into the corresponding break frequency
into the corresponding break frequency 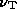 .
.
In this paper I present theoretical colour-colour diagrams for a
variety of realistic spectra such as those presented in Paper
I, and compare them to the particular case of Cygnus A.
Up to:
___________________________________
Peter Tribble, peter.tribble@gmail.com
 because its pitch
angle has been continually randomized by the scattering. The total
losses are then the instantaneous losses B^2sin^2
because its pitch
angle has been continually randomized by the scattering. The total
losses are then the instantaneous losses B^2sin^2 , averaged over all pitch angles
to give B^2<sin^2
, averaged over all pitch angles
to give B^2<sin^2 >, and are independent of an electron's
current pitch angle. There is a sharp cutoff in the energy spectrum at
a break energy
>, and are independent of an electron's
current pitch angle. There is a sharp cutoff in the energy spectrum at
a break energy 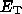 that is independent of
pitch angle or viewing orientation. The resulting spectrum is sharply
cut off at a frequency
that is independent of
pitch angle or viewing orientation. The resulting spectrum is sharply
cut off at a frequency 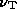 = c_1 B
= c_1 B
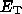 ^2 sin
^2 sin where B is the field strength and
c_1 is a constant (Pacholczyk 1970). There is little variation of the
spectrum with viewing angle so that averaging over different
orientations of the field gives a total spectrum that retains the sharp
cutoff.
where B is the field strength and
c_1 is a constant (Pacholczyk 1970). There is little variation of the
spectrum with viewing angle so that averaging over different
orientations of the field gives a total spectrum that retains the sharp
cutoff.